

Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-08-04 Origin: Site
Tungsten carbide punches work better than regular tools in many factories. The tool’s material is very important in making things. Companies need punches that are strong and last a long time. Tungsten carbide punches are very hard and do not wear out fast. This makes them a top choice in car, airplane, mining, and building jobs.
The world market for tungsten carbide punches gets bigger every year. This is true in North America and Europe. These places need punches that work well for new ways of making things.
Industrial Sector | Tungsten Carbide Punch Usage | Market Share / Growth Rate |
|---|---|---|
Manufacturing | Uses punches to shape metal and plastic | 10% of cutting tools market (2023) |
Automotive | Punches for car body and engine parts | Main user, growing fast |
Electronics | Punches for very exact machine work | Grows the fastest |
Mining & Construction | Punches in drill bits and tough tools | 37.6% market share (2024) |
Aerospace & Defense | Punches for turbine blades and strong drills | Important, but less measured |
Tungsten carbide punch technology helps make better tools today. It gives tools great strength and accuracy.
Tungsten carbide punches last longer than steel punches. This means factories stop less and save money. These punches stay sharp and exact after many uses. This helps factories make good and correct parts. Tungsten carbide punches fight wear, heat, and pressure better than steel tools. This makes them great for hard jobs. Using tungsten carbide punches helps workers do more by changing tools less. Machines also stop less in many industries. Taking care of and recycling tungsten carbide punches helps the environment. It also makes the tools last longer.
Tungsten carbide punches are special tools used in factories. They help shape, cut, or form different materials. These punches are made from tungsten carbide. This is a compound made by mixing tungsten and carbon at very high heat. Factories use CNC machines to make punch pins with exact shapes and sizes. The process uses grinding, polishing, and wire EDM machining. Each punch pin is made very accurately, often within ±0.002mm. Carbide punches are not like regular steel punches. They use a mix of tungsten carbide, cobalt, titanium tungsten carbide, and nickel. The mix changes for each job. Some punches have up to 75% tungsten carbide. Others use more titanium tungsten carbide or cobalt. This mix gives each punch its own hardness and toughness.
Tungsten carbide punch pins are different because their chemical makeup can change. Makers pick the right grade for each job. This makes these punches more useful than regular tools.
Tungsten carbide punches have many important features. They are almost as hard as diamond, with a Mohs hardness of about 9. Their density is 15.6 g/cm³, which is much higher than steel punches. Carbide punches also have very high wear resistance. They last longer and keep their shape after many uses. The table below shows how tungsten carbide punch pins compare to steel punches:
Property | Tungsten Carbide Punches | Steel Punches (Typical) |
|---|---|---|
Hardness (Mohs) | ~9 (near diamond hardness) | ~4-8 |
Density (g/cm³) | ~15.6 | ~7.8 |
Wear Resistance | Very high | Lower |
Durability | High | Lower |
Carbide punches do not bend easily and work well under high pressure. Their hardness lets them punch through tough things like metal, plastic, and ceramics. Tungsten carbide punch pins stay strong even at high temperatures. This makes them good for hard jobs. Factories need special machines and careful steps to make these punches. Their hardness and brittleness mean the surface and inside must be controlled well. This care helps stop chipping and makes each punch pin last longer than regular punches.
Tungsten carbide punches are different from steel punches. They have special material features. Factories pick carbide punches for jobs that need to be exact and last a long time. Here are some main differences:
Tungsten carbide punches are much harder than steel punches. They last longer and work well for tough stamping jobs.
Carbide punches keep their sharp edges for a long time. But they can break if hit too hard, so they are not good for heavy impacts.
Steel punches, like D2 or A2, are tougher and can take more hits.
Carbide punches are used in aerospace and electronics for very exact stamping.
Steel punches cost less and are good for most stamping jobs.
Property | Tungsten Carbide | Traditional Steel (e.g., High-Speed Steel) |
|---|---|---|
Hardness | Much higher; stays hard up to 1000°C | Lower; gets softer at high heat |
Wear Resistance | Very high; does not wear out fast | Good, but not as high as tungsten carbide |
Temperature Stability | Stays strong at high heat (up to 1000°C) | Not as good; gets soft when hot |
Brittleness | More likely to break if hit hard | Tougher; can take more hits |
Cost | Costs more because it is harder to make | Cheaper; used in many factories |
Typical Applications | Used for exact, tough, and high-tech jobs | Used for regular machines, cutting, and forging |
Tungsten carbide punches have tiny hard grains mixed with cobalt. This makes them hard and a little tough. Steel punches have a simpler mix. They are not as hard but can bend more. This is why carbide punches last longer but might chip if hit too hard.
Tungsten carbide punches work better than steel punches in stamping. They do not wear out fast. They can last up to 20 times longer than most steel punches. This means factories do not have to replace them as often. Factories using carbide punches have fewer tool problems and less time when machines stop.
Material Type | Performance Metric | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|
Tungsten Carbide Particles in MMC | Wear resistance and lifespan | FTC particles help stop wear, so tools last longer. |
Steel 1.2365 (WLV) | Wear resistance and lifespan | This steel resists wear and bending; lasts longer than 1.2344 and Unimax steels. |
Steel 1.2344 and Unimax | Wear resistance | These steels wear out faster and lose height quicker than 1.2365 and tungsten carbide. |
Steel W360 | Wear resistance | Wears out slower than 1.2344 and Unimax, like 1.2365. |
Tungsten carbide punches are much harder than steel punches. The chart below shows how much harder they are:
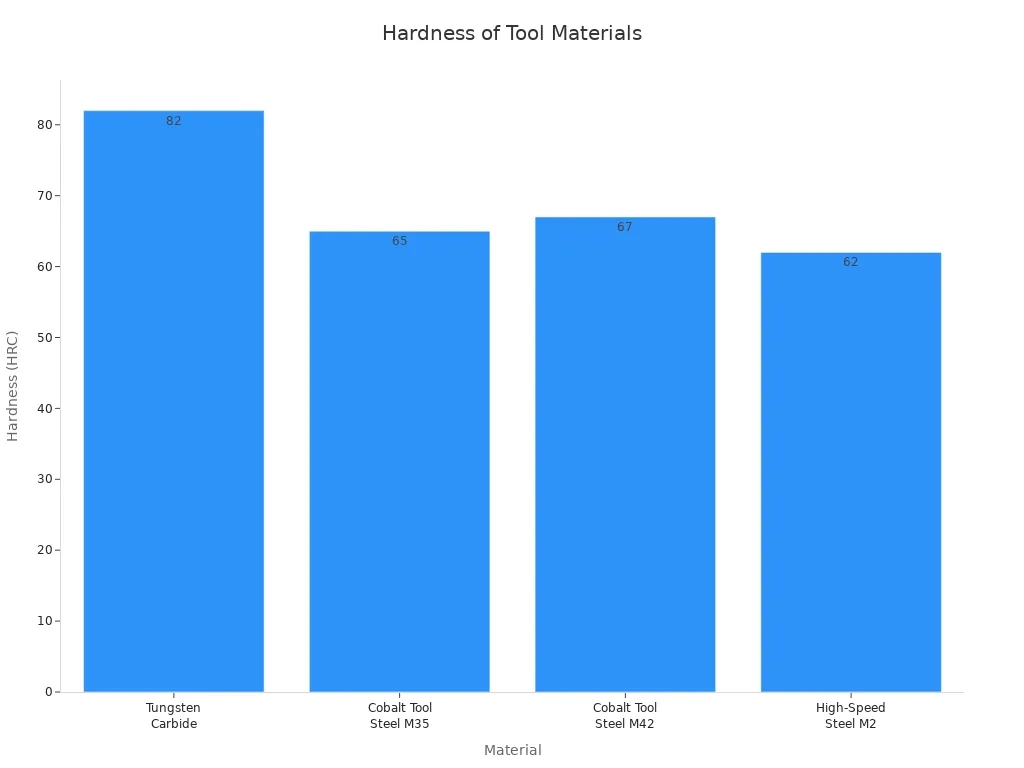
Note: Hard metal punches like tungsten carbide are best for jobs that need to be very exact and last a long time. Steel punches are better for jobs with lots of hits or when saving money is important.
Carbide punches are known for lasting a long time in factories. Many companies pick these punches because they work well for a long time. Tungsten carbide punch tools can be used again and again in busy factories. They keep their shape and sharpness after many uses. This is because of how tungsten carbide is made. It mixes hard tungsten with a binder like cobalt. This makes a punch that does not crack, chip, or bend easily.
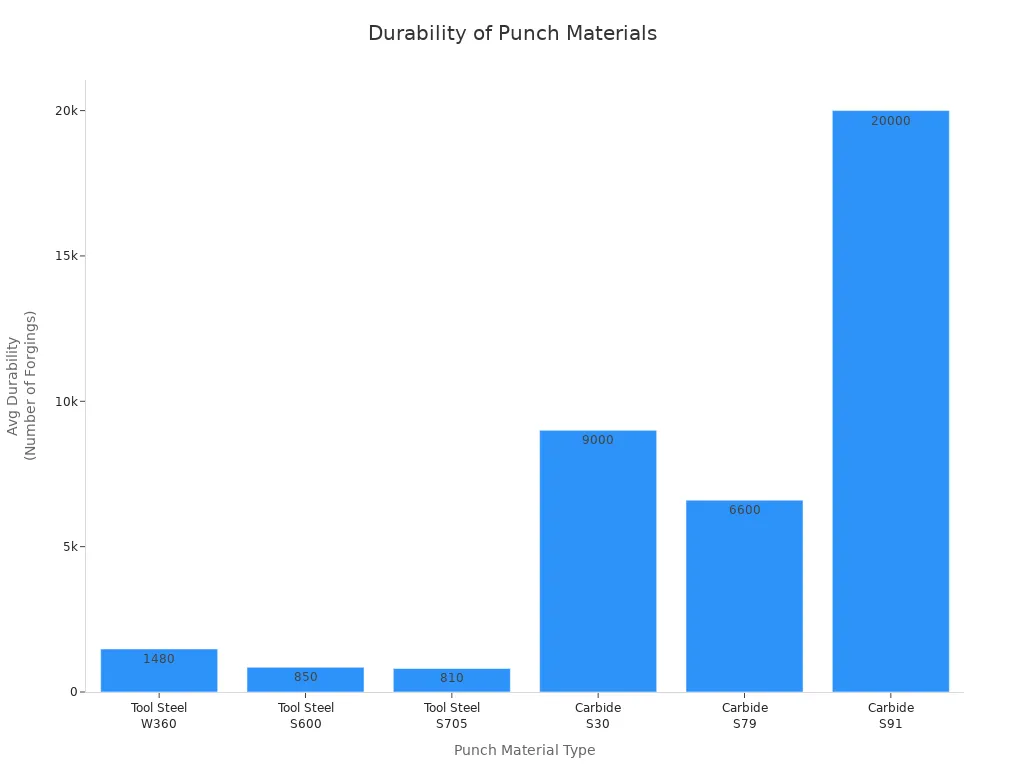
A chart shows that carbide punches last much longer than steel punches:
Punch Material | Service Life Multiplier (vs. Steel) | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|
Carbide Punch Blanks | 10 to 20 times | High wear resistance, impact strength, durability |
Steel Punches | Baseline (1x) | Lower upfront cost, suitable for short runs |
Carbide punches can last 10 to 20 times longer than steel punches. This means factories do not need to change them as often. This saves both time and money. In busy factories, cemented carbide blanking dies can last up to 50 times longer than steel dies. The chart below shows how much longer carbide tools last than steel tools:

Longer tool life means machines stop less often. This helps companies keep working without many breaks.
Carbide punches also work well in tough jobs. They can handle high heat and heavy pressure. This makes them good for stamping, forming, and cutting hard things. Because they last so long, factories do not need to buy new ones often. Over time, this saves a lot of money, especially in places where machines run all day.
Wear resistance is a big reason why people use carbide punches. These punches can handle rough materials and fast work without wearing out. Tungsten carbide punches are almost as hard as diamond. This makes them very good at fighting wear and scratches. They keep their sharp edges and size for a long time.
Tungsten carbide punches are very hard, about 9 on the Mohs scale. This is just under diamond and much harder than most tool steels.
Carbide punches keep their shape and sharpness after lots of use. They work well even when there is a lot of heat and rubbing.
Because they last longer, factories have less downtime and get steady results.
Carbide punches do not get soft from heat. They work well in fast or hot jobs where steel punches might not.
Better wear resistance means smoother finishes and fewer tool changes. This saves money, even if carbide punches cost more at first.
Tungsten carbide punch tools are very hard and do not wear out fast. Their strong build lets them work in tough places where steel punches would break down. Factories using carbide punches see fewer mistakes and better products. The punches keep their edge and shape, even on hard things like stainless steel or titanium.
Taking care of carbide punches helps them last longer. Workers should be gentle to stop cracks or chips. Using the right tools to put in or take out punches stops damage. Checking for cracks or wear helps find problems early. Good care means cleaning, drying, sharpening, and oiling the punches. Storing them in dry places keeps them safe from water damage.
Carbide punches need careful handling, but they last longer. This means fewer stops and smoother work in factories.
Precision is a main reason factories use tungsten carbide punches. These punches give accurate and steady results, even in hard jobs. High-precision carbide punches stay sharp for a long time. Their hardness keeps them from getting dull, unlike steel punches.
Tungsten carbide punches stay sharp after lots of use. Their hardness keeps them from wearing down as fast as steel punches.
Because they last longer, factories save time and money. This helps make work faster.
Carbide punches do not bend or chip easily. This means products stay the same and are made well.
Using tungsten carbide punches helps factories make things with tight measurements. There are fewer mistakes and less fixing needed than with steel punches.
Special coatings can make carbide punches even more precise and tough. This helps make better products and more of them.
High-precision carbide punches are made with special machines and good materials. This lets them be very exact and steady. Electronics and other industries use these punches for small, careful jobs. Accurate stamping helps make high-quality products and less waste.
Picking good tungsten carbide punches from trusted makers helps factories work better. Taking care of the punches makes them last longer and keeps work steady. This means fewer mistakes and less fixing, which saves time and money.
Being precise in making things leads to better products and happy customers. Carbide punches help companies meet high standards and give good results.
Carbide punches also help save money over time. Their hardness and wear resistance mean they last much longer than steel punches. This means less fixing or changing tools. Less downtime means machines keep working, and workers do not have to stop as much. Even though carbide punches cost more at first, they save money because they last longer.
The SnoShock™ Shock Absorbing Carbide Insert Cutting Edge System lasts 2 to 4 times longer than regular carbide systems. Its special design stops breaking and cuts down on shaking.
Customers say they have less downtime and fixing because these inserts can take hits that would break others. This helps work go faster and saves money.
Tungsten carbide punches are very important in today’s factories. They are needed in jobs where things must be made fast and right. These punches help companies make the same good parts every time. They also help stop machines from breaking down. This keeps work going and keeps products good. The next parts show how these punches are used in making things, stamping metal, and other special jobs.
Factories need tools that can be used many times and still work well. Tungsten carbide punches are picked because they are very hard and do not wear out fast. These punches are used in car, electronics, and airplane factories. They can stamp things quickly and still stay sharp.
Factories use these punches for many jobs. They punch holes, shape, and form things made of metal, plastic, ceramic, and other stuff. The punches stay sharp and the right size even after being used a lot. This helps factories keep working without stopping.
Car factories use these punches to make holes in car parts.
Electronics factories use them to stamp small parts like connectors.
Airplane companies use them to shape and clean fasteners so they are safe.
Medical companies use them to make tiny holes in tools and implants.
Tungsten carbide punches last longer and need less fixing. They do not need to be changed as much. This means factories save time and money. When factories use these punches, they often see better and more even products.
Tip: Picking the right kind of tungsten carbide for each job helps the punches last longer and work better.
Metal stamping tools must work fast and make things the right size. Tungsten carbide punches are very good at this. They are used in jobs where the punch is hit many times and must not break.
Some jobs for these punches are:
Making blind holes in thin steel sheets
Making holes for screws in car and electronics parts
Punching tiny oval holes for antennas and small parts
Shaping and cleaning fasteners in airplanes
Punching thin metal for batteries and sensors
Special punches can make different shapes like hexagons or ovals. Some punches help line up holes. Others can punch and shape at the same time to save time.
Tungsten carbide punches work better than steel punches in fast stamping. They stay sharp after many uses. This means less time spent changing tools. Factories get more work done and the parts are always the same.
Application Area | Tungsten Carbide Punch Role | Benefit to Productivity |
|---|---|---|
Automotive | Punching holes in body panels, engine parts | Fewer tool changes, higher output |
Electronics | Progressive stamping of connectors, terminals | Tight tolerances, smooth finish |
Aerospace | Forming, deburring, and punching fasteners | High precision, durability |
Medical Devices | Punching holes in surgical tools, implants | Consistent quality, long tool life |
These punches are also used in progressive stamping. This means many steps happen at once. It helps make more parts faster and with less waste. The punches keep their shape so every part is made right.
Note: Factories using these punches in progressive stamping can use each tool up to 1.5 million times. The finished parts are smooth and have no scratches. This is very important when making lots of parts.
Tungsten carbide punches are not just for metal. They can punch, shape, and form plastic and ceramic too. These punches work well in jobs that need both strength and accuracy.
Feature | Description |
|---|---|
Hardness | Tungsten carbide punches are very hard. They do not bend or break when stamping hard things. |
Wear Resistance | They stay sharp and the right size even after lots of use. This makes them last longer. |
Precision | They are made very carefully, so every punch is the same. |
Applications | They can punch, stamp, shape, and form many things, not just metal. |
Cost-effectiveness | Even though they cost more at first, they last longer and save money over time. |
Factories use these punches for:
Making holes in plastic cases for electronics
Stamping ceramic parts for sensors and medical tools
Shaping new materials for cars and planes
Making small shapes for jewelry and watches
These punches give the same good results on many materials. They make sure every hole is the right size, even in hard jobs. Because they last longer, factories do not need to buy new ones as often. This saves time and money.
Tungsten carbide punches also help the environment. They last longer, so fewer are thrown away. Recycling old punches saves resources and helps nature.
Callout: It is important to handle and recycle these punches the right way. Special companies can get back the metals. This helps save resources and keeps the earth clean.
In car factories, these punches help save money and time. They make better parts and last longer in tough jobs like punching and shaping.
Electronics factories use these punches to make smooth metal parts. Some punches last up to 1.5 million uses. Coated punches last even longer and make parts look better.
Airplane companies use these punches to shape and clean fasteners. The punches work well even when it is hot or hard, so every part is safe and good.
Tungsten carbide punches help factories work better in many ways:
They last longer, so machines stop less often.
They are always accurate, which helps make parts fast.
Fewer tool changes mean more time making things.
They can be used on many materials, so factories can do more jobs.
Pro Tip: Buying good tungsten carbide punches helps factories save money and work better in the end.
Tungsten carbide punches are great, but they must be managed well. Throwing them away the wrong way can hurt the earth. Factories should recycle them to save materials and stop pollution. Recycling also means less mining is needed.
Mining for tungsten can hurt nature if not done right.
Recycling old punches helps protect the earth and supports green factories.
Because these punches last longer, less waste is made.
Tungsten carbide punches have changed how things are made. They are very hard, last a long time, and are very accurate. They are the best choice for fast stamping and making holes in many materials. These punches help make better products, save money, and need less fixing. By using them, companies can do better work, help the earth, and stay ahead in today’s busy world.
Tungsten carbide punches and punch pins are very hard and strong. They do not wear out fast and can last a long time. These tools work much longer than steel punches. This helps factories save money and have fewer stops. Many industries use punch pins for careful jobs in mining, cars, and airplanes. Experts think new punch pins will use smart materials and special coatings. They will also be easier to recycle. This will make them work better and be better for the planet.
New punch pins will help factories work faster, safer, and cleaner.
A punch pin is a tool used to make holes or shapes in materials. Factories use punch pins in stamping, forming, and cutting. Punch pins often use tungsten carbide for extra strength and long life.
Factories pick tungsten carbide punches because they last longer and stay sharp. These punches resist wear and heat. Workers can use them many times without losing accuracy.
Tungsten carbide rods give punch pins their hardness and strength. The rods help punch pins keep their shape after many uses. This makes them ideal for tough jobs in manufacturing.
Yes, punch pins can work with metals, plastics, and ceramics. Tungsten carbide punches handle hard and soft materials. They help factories make many types of products.
Workers should clean and store punch pins in dry places. They should check for cracks or chips before use. Careful handling helps punch pins last longer and work better.
